Devolved: Unity through Evolution, Diversity and Connection
A series of work by artist Cade Kegerreis
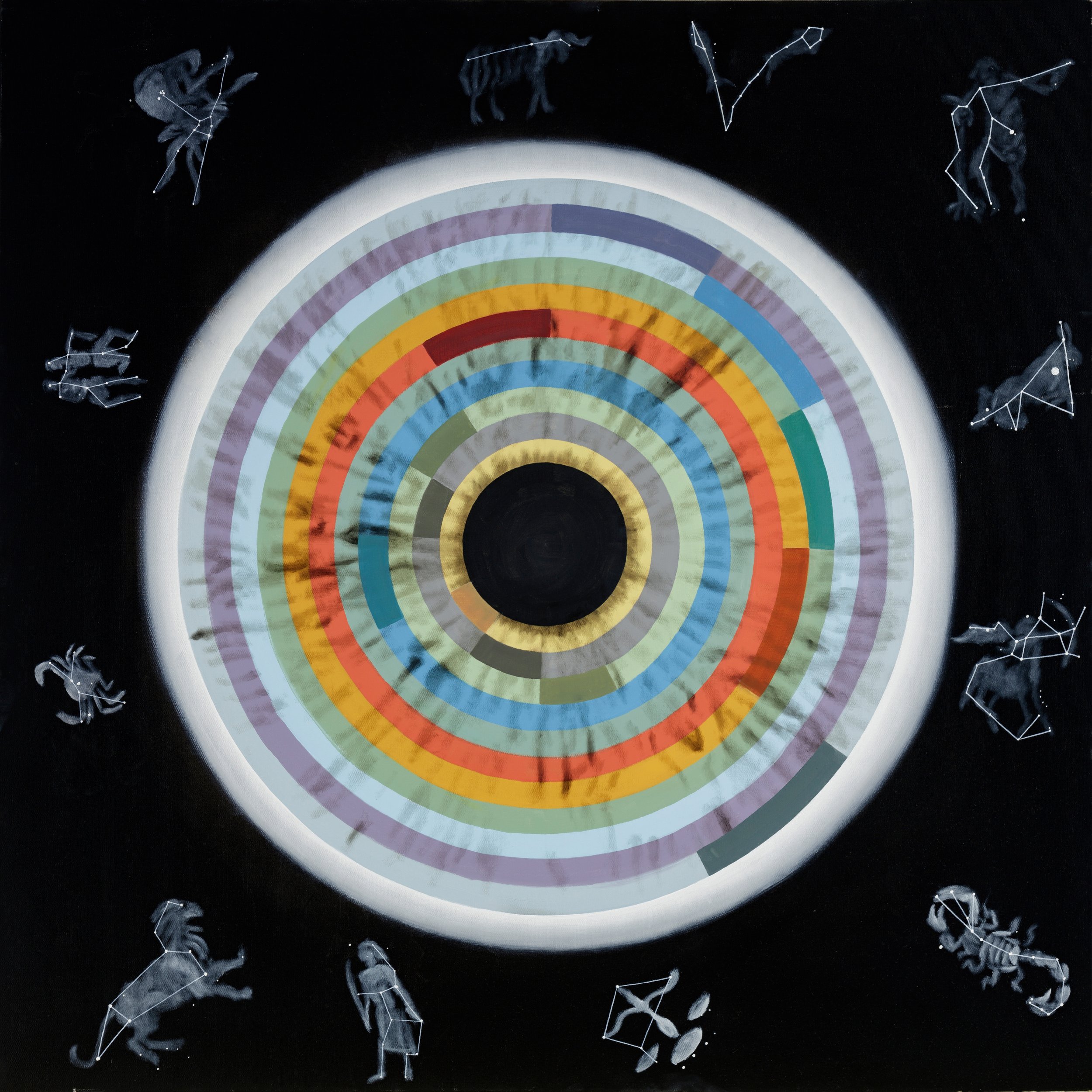
Astrology
From the earliest civilizations, a great importance was placed on the night sky to explain our place in the universe. Ancient astronomers developed the framework for what evolved into mythology and eventually religion to offer an explanation of humanity. Many use the celestial guides to understand personal traits and energies. There is an overall focus of learning how to see yourself before attempting to see others.
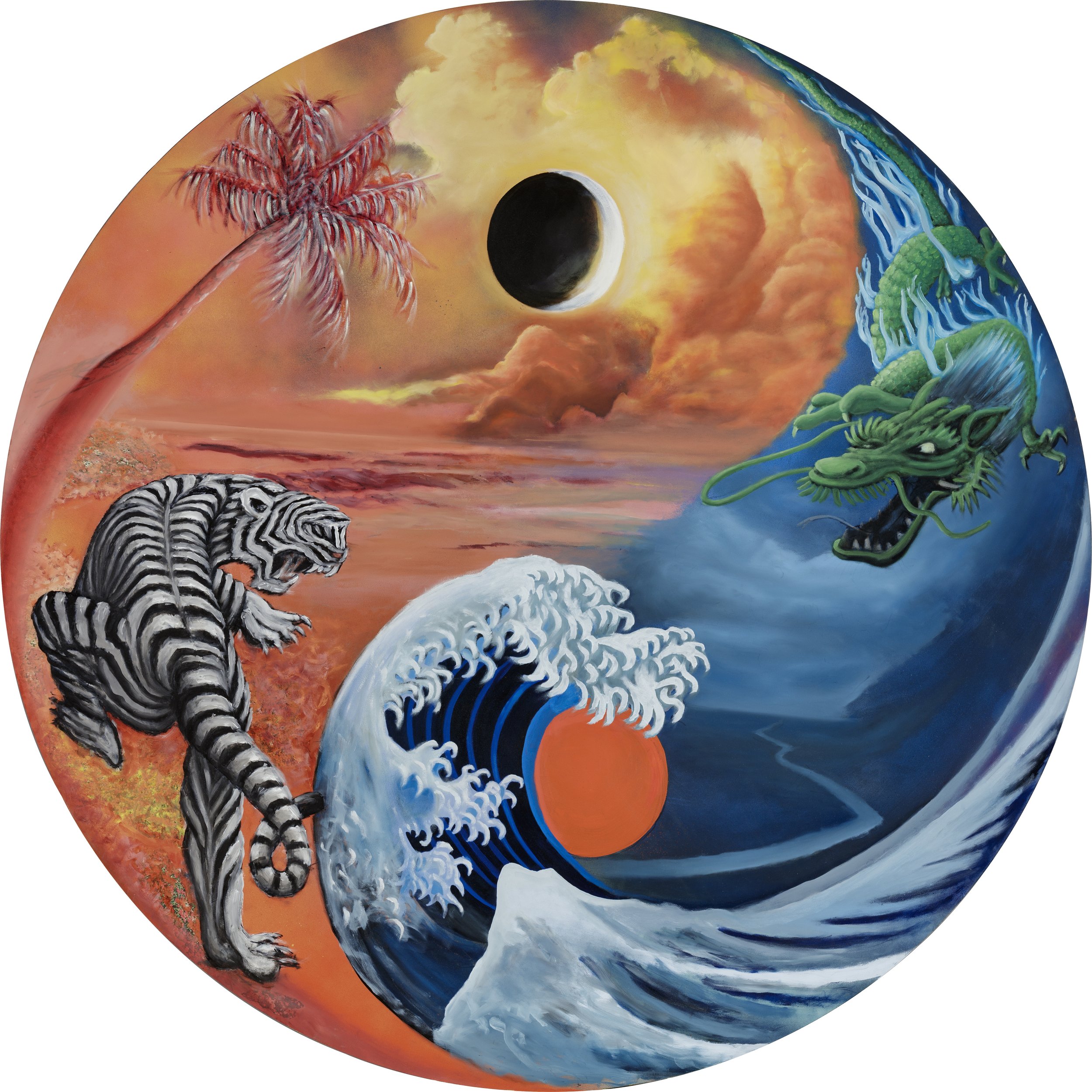
Duality
The yin and yang of early Chinese culture represent a form of dualism. Male and female, light and dark, active and passive, motion and stillness; a few of the countless examples of two parts that make up a whole. There is inter-connectedness of the opposite forces that create balance and harmony. Many religions have gods of good and evil that symbolize the idea of dualism. The contrasting and complementary nature of the parts allow for a continual flow that is a unifying force within all things.
Tree of Life
The tree of life is an idea shared across almost every culture and civilization since the beginning of recorded history. A few of the most known examples are the Mayan tree, the tree in the Garden of Eden, the Norse tree “Yggdrasil”, the Indian (Hindu) Bhagavad Gita, and the Ancient Egypt tree. All of these trees of life hint to the idea of immortality and transcendence. The spiritual immortality that heaven is thought to provide is the “goal” of modern religions. When you pick apart what these different practices teach, they are remarkably similar- both in morals and the stories used to convey the ideal way of living. No matter the religion, the purpose is to become more righteous to attain salvation.
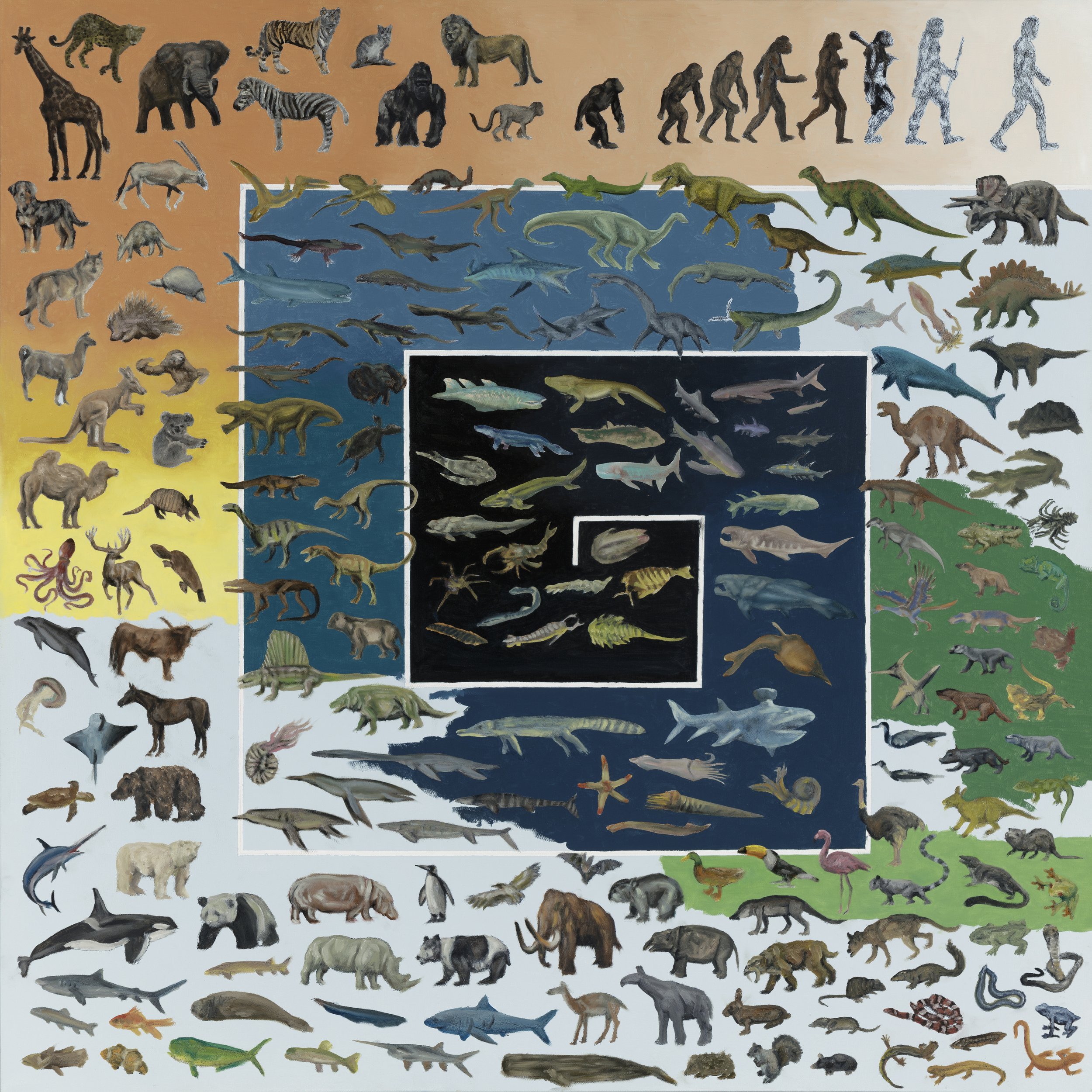
Animal Evolution
Animals evolved in the sea starting 1 billion years ago from the simplest single celled organisms. The lack of the Earth’s ozone layer made it impossible for animals to live beyond the waters for another 600 million years. Once photosynthesis increased the oxygen levels of the atmosphere, the ozone layer formed, allowing the first land visitors. Millions of years of evolution slowly diversified the types of life, mostly being invertebrate sea creatures. Animals evolved their ways of reproducing that did not involve water, endoskeletons and exoskeletons. These changes allowed them to move about on land. The amniotic egg allowed early reptiles to go past the shores and colonize dry regions. This gave way to the eventual evolution of birds, mammals, and reptiles. The different groups continued to diversify and evolve as time and environment shaped them.
Civilizations
Africa is believed to be the original birthplace of man. The earliest human-related fossils dating back millions of years have been recovered there. However, starting hundreds of thousands of years ago modern humans began to inhabit beyond Africa and into parts of Europe and Asia. These ancestors lived as nomads, depending on the land to provide them with the means to survive. It wasn’t until them Upper Paleolithic period (~50-12,000 years ago) that the earliest forms of civilization developed. Shelter and tools were important factors in this advancement. The evolution of tools and the skills to use them enabled groups to live more comfortably. This comfort allowed more time and energy to be devoted to other things. This was the beginning of culture. It was largely displayed by art, dress, and communication, anything that wasn’t necessary for survival slowly evolved to further the identity of these specific groups. Following the end of the Pleistocene Epoch (Ice Age) 11,700 years ago, groups of people started congregating in larger numbers due to the emergence of agriculture. It is with this key factor that sustained the exponential growth of modern civilization.
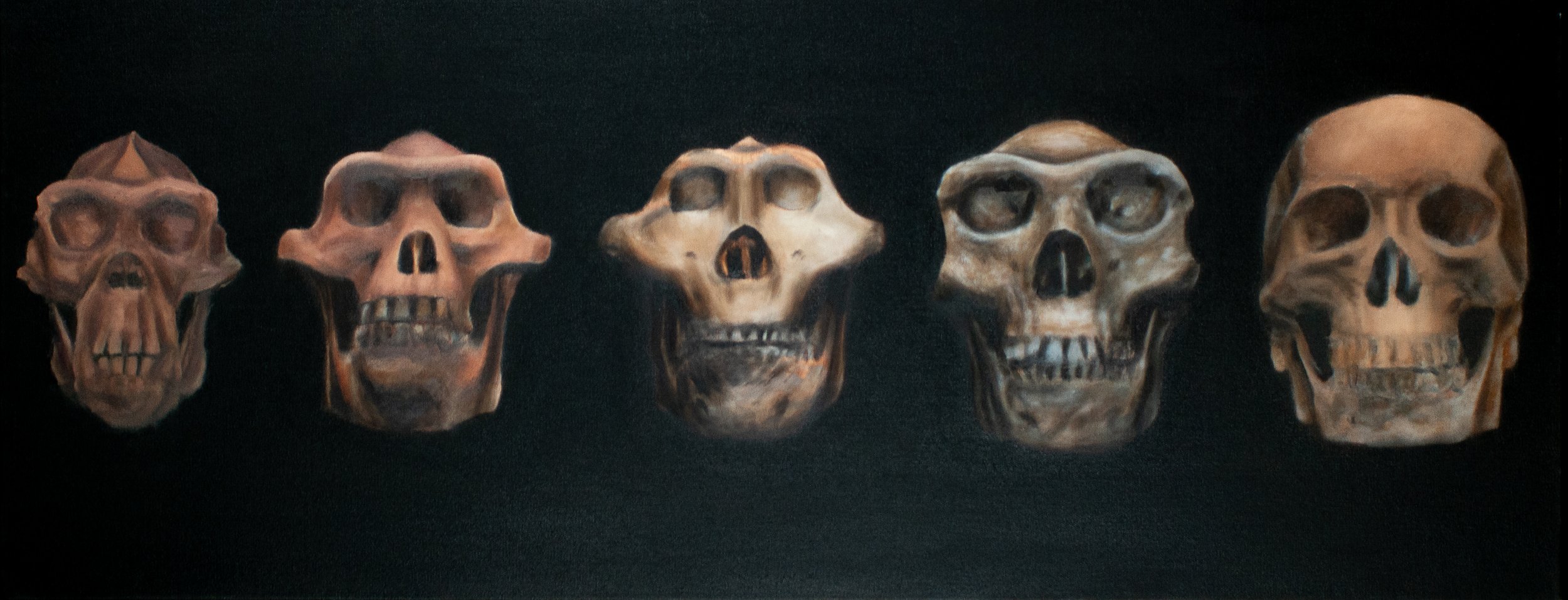
Human Evolution
The evolution of the hominid skull was largely impacted by the diets that affected brain size. It is also thought that the structure of the face evolved to minimize injury and protect the head during fights with other humans. As humans developed, their brain capacity increased and the cranial cavity grew. The teeth and jaw also changed in relation to our evolving diet.
Human Spectrum
Similar to how animals evolved over hundreds of millions of years, modern humans have developed certain traits to live more successfully in their environment. All humans on Earth can link themselves back to ancestors that began walking upright just a few million years ago. As people continued to move abroad and inhabit different parts of the world, their bodies changed. The humans of African climates elongated to stay cool, while those in colder places developed more compact body shapes to retain more heat. Within the three branches of near humans, homo erectus and the Neanderthals became extinct before fully adapting to the most recent climate changes in the past 100,000 years. Skin pigmentation is another key trait of human evolution. The melanin of the skin is simply an adaptation to protect against the harmful UV rays from the sun. The same is true for the iris color in the eye. The notion of “race” is a created idea of society, not a biological trait.
Art History
The act of creative expression dates back to the earliest forms of civilization. From the first cave paintings made over 50,000 years ago, people have had the inner desire to record what they see, do, and think. Art is created to convey meaning, show importance, or serve usefulness through visual experience. As society changed, art went through waves of appreciation. Art of the past 500 years has mainly been used to memorialize political figures, noble families, and praise religious beliefs. Our current time compliments artwork based on aesthetic, though it can be used to tell a much more in-depth story.
Science
Science is all encompassing. From the galaxies in our universe, down to the molecular level of all things on Earth, the rules of science govern the way things are. The interest in understanding the unknown is the root of growth. The knowledge of the natural world and its process has built the blocks needed for our current societies to exist. From medicine to transportation, countless years of human experience and research have allowed us to live the lives we do. Technology impacts our life more today than ever before. With the exponential advancements that take place, it is difficult to imagine what our future will hold.
Spiral of Time
Life is often a chaotic spiral. Though you may feel pulled in so many directions, time is the only constant that keeps going forward. Mistakes are often the best way to learn a lesson. Experience will likely get you further than knowledge alone. But the understanding and willingness to accept it all will allow you to keep moving with ease. Learn from the past. Embrace the present. No one knows what the future holds.
Amalgamation
We live in a very fast-paced world. Instant gratification, communication, and results are normal desirables that weren’t even possible until the very recent past. Allow yourself some time to slow down. Take it all in. Smell the roses. The troubles of the world cannot be fixed instantly. The troubles you see within yourself cannot be fixed overnight. Use this as a reminder to focus on yourself. Give yourself the opportunity to grow. Gain some knowledge. Share some love. Spread some peace. You, and everyone around you are just trying to figure it all out. We are all out in the middle of space, living on this Earth, trying to make the most of what we have. We are all one in the same. From evolution we came, diverse we are, and connected we will always be. We are all united.”